The documentation you are viewing is for Dapr v1.10 which is an older version of Dapr. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Configuration overview
Consuming application configuration is a common task when writing applications. Frequently, configuration stores are used to manage this configuration data. A configuration item is often dynamic in nature and tightly coupled to the needs of the application that consumes it.
For example, application configuration can include:
- Names of secrets
- Different identifiers
- Partition or consumer IDs
- Names of databases to connect to, etc
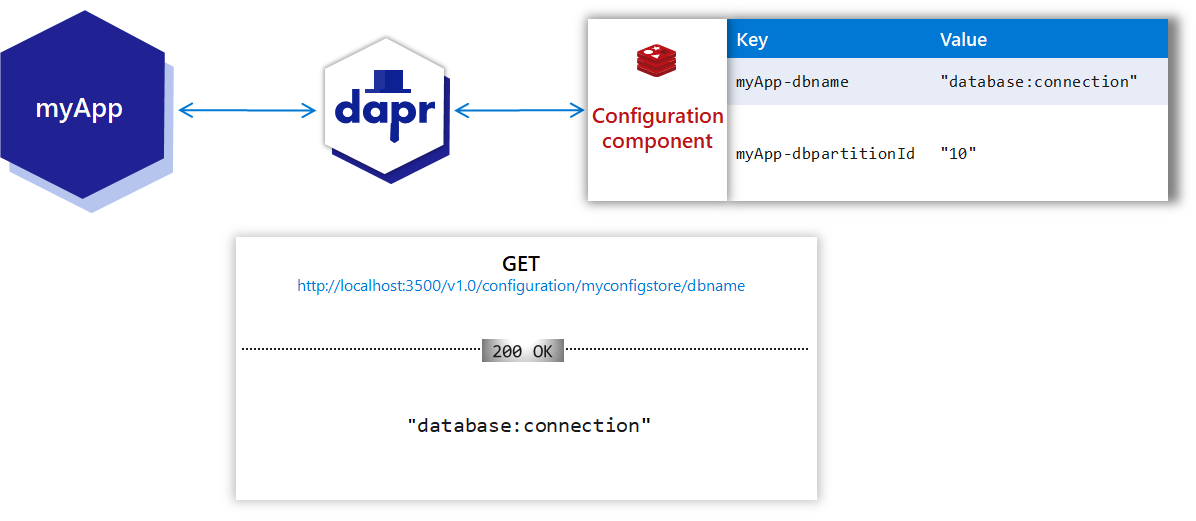
Usually, configuration items are stored as key/value items in a state store or database. Developers or operators can change application configuration at runtime in the configuration store. Once changes are made, a service is notified to load the new configuration.
Configuration data is read-only from the application API perspective, with updates to the configuration store made through operator tooling. With Dapr’s configuration API, you can:
- Consume configuration items that are returned as read-only key/value pairs
- Subscribe to changes whenever a configuration item changes
Note
The Configuration API should not be confused with the Dapr sidecar and control plane configuration, which is used to set policies and settings on Dapr sidecar instances or the installed Dapr control plane.Try out configuration
Quickstart
Want to put the Dapr configuration API to the test? Walk through the following quickstart to see the configuration API in action:
| Quickstart | Description |
|---|---|
| Configuration quickstart | Get configuration items or subscribe to configuration changes using the configuration API. |
Start using the configuration API directly in your app
Want to skip the quickstarts? Not a problem. You can try out the configuration building block directly in your application to read and manage configuration data. After Dapr is installed, you can begin using the configuration API starting with the configuration how-to guide.
Next steps
Follow these guides on:
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.